Tourette’s Syndrome (TS)
- is a genetic neuropsychiatric disorder, characterized by physical and vocal tics, and associated with the exclamation of obscene words or socially inappropriate remarks. Tics are repetitive and non-rhythmic movements of discrete muscle groups and are formed due to genetic mutation that disrupts the production of histamine in the brain and are primarily caused due to the disturbance in the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, which carry nerve signals from cell to cell.
- increases the risk of hyperactivity disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder in children. Blinking, frowning, jerking, and foot stamping are some of the additional symptoms of Tourette’s syndrome.
- primarily affects children aged between 6 years and 17 years with the average onset age of 3 and 9 years;
- occurs in people from all ethnic groups; occurs in males 3 to 4 times more often than females; and is twice as likely in Non-Hispanic white children than in Hispanic and non-Hispanic black children.
The U.S. dominates the global Tourette’s syndrome market where, as per the data of the CDC study, 1 of every 360 (0.3%) children 6-17 years of age have received a diagnosis of TS, and that incidence rate is expected to expand in the future. Europe is the second-largest market and is expanding there owing to its high incidence rate and is also expanding in the Asia Pacific and Latin America due to increasing awareness among patients.
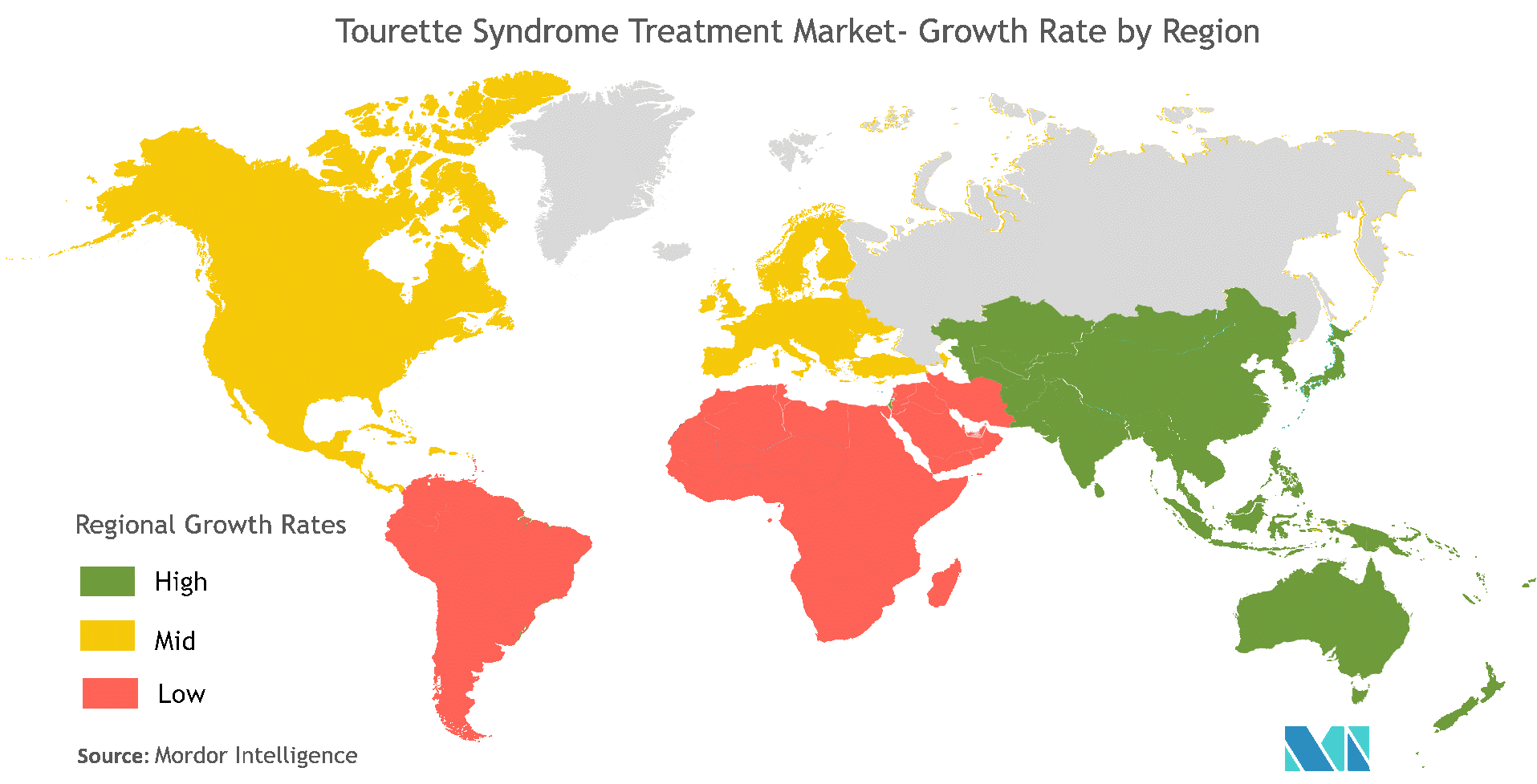
There are currently NO commercially approved drugs for the treatment of TS in the market but many companies are working on the research and development of new drugs to treat the disease so the drug pipeline is quite robust, and many drugs are expected to launch during the period of forecast (2020-2027). Technavio has estimated that the global Tourette’s Syndrome drugs market will progress at a CAGR of 5% ($98.77M) over the next few years suggesting that the size of the drug market is approximately $40B.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
- is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people in the world. It takes its name from the Greek word apnea, which means “without breath.” People with sleep apnea literally stop breathing repeatedly during their sleep, often for a minute or longer and as many as hundreds of times during a single night. It occurs when the muscles relax during sleep, causing soft tissue in the back of the throat to collapse and block the upper airway which may be caused by either complete obstruction of the airway (obstructive apnea) or partial obstruction which can both wake one up. Of these, obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common;
- is most prevalent in individuals with factors that include being older, being male, being a minority race, having a high body mass index, having a large neck circumference, having craniofacial abnormalities, being menopausal, and having health behaviors such as smoking and alcohol use.
The standard therapy of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is efficient in improving OSA and in reducing its associated comorbidities but patients often cannot tolerate CPAP, which can produce general discomfort or troublesome nasal symptoms leading to poor adherence. As such, alternative options need to be developed and pharmacological therapies are an obvious approach. Furthermore, Frost & Sullivan estimates the prevalence of OSA to be 12% or 29.4 million of the U.S. adult population with nearly 80% of the population undiagnosed which demonstrates the unmet medical need. The global Obstructive Sleep Apnea market size was found to be US$221.8M in 2017 of which the USA accounted for 75%. The market is estimated to be increasing by 4.7% CAGR during the study period (2017–2030) which would put the market size at approximately US$400M by 2030.
Alzheimer’s
- is the most common form of dementia, (worldwide about 50 million people have some form of dementia)
- is a progressive brain disease that slowly destroys memories and thinking skills. Symptoms usually start with difficulty remembering new information and, in advanced stages, symptoms include confusion, mood, and behavior changes, and inability to care for one’s self and perform basic life tasks.
- ranks as the third leading cause of death, after heart disease and cancer,
- affects approximately 5.7 million people in the U.S. currently (200,000 people under age 65 have early-onset Alzheimer’s disease) and that number is projected to triple to 16 million by 2050,
- doubles about every five years after age 65 and, after age 85, the risk reaches nearly 50%,
- will adversely affect Latino and African American populations as their “senior citizens” will grow 224% and 114%, respectively, by 2030, compared to a 65% growth rate for non-Latino white Americans and
- will affect African Americans twice as likely as white Americans and Latinos by 1.5 times.
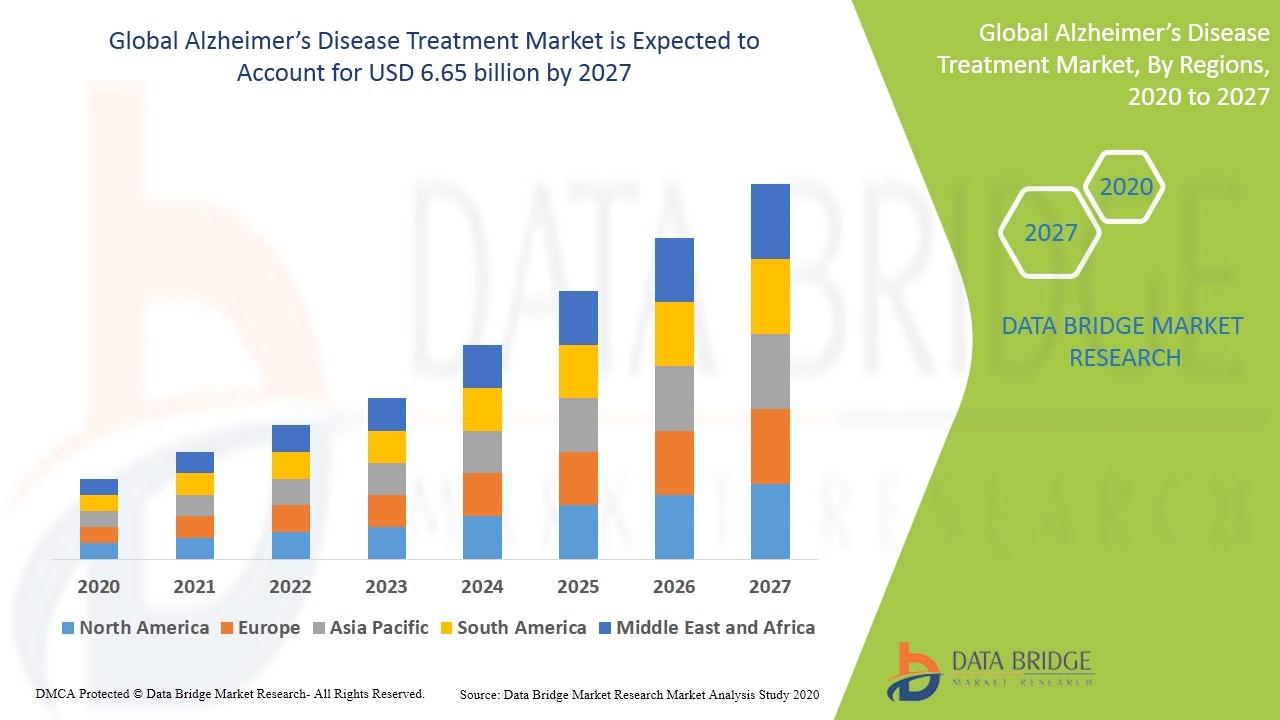
According to research and consulting firm, GlobalData, disease-modifying treatments for Alzheimer’s Disease as well as novel symptomatic therapies with innovative mechanisms of action will enter the arena between now and 2030. Data Bridge Market Research expects that the Alzheimer’s disease treatment market size will grow at a CAGR of 8.29% between now and 2027 and reach US$6.65B by then.
 munKNEE.com Your Key to Making Money
munKNEE.com Your Key to Making Money